If you’re serious about building long-term search traffic to your blog or website, you need more than just good content. You need clarity — on what’s working, what’s broken, and where to focus next. That’s where Google Search Console comes in.
Google Search Console (GSC) won’t magically boost your google rankings on Search Engine Results Page (SERP), but it gives you the data and diagnostics you need to make smart decisions. From fixing indexing issues that block visibility, to tracking how your content performs in search, GSC is a foundational tool — especially when combined with solid keyword research, content optimization, technical SEO, and off-page efforts like backlinks.
GSC is a free tool from Google that helps you monitor, optimize, and troubleshoot your blog’s performance in search results, making it an essential part of your SEO analytics tool kit. Leveraging GSC can uncover hidden ranking opportunities, fix critical errors, and drive sustainable organic growth.
In this blog post, you’ll learn all that you need about Google Search Console : how to set up and use Google Search Console (GSC) to improve your blog’s SEO. We’ll cover everything from submitting sitemaps and fixing indexing errors, to tracking keyword performance, analyzing search queries, and improving click-through rates — all using data directly from Google. Whether you’re just starting your blog or trying to grow your search traffic, this guide will show you how to turn GSC from a confusing tool into a powerful SEO asset. Plus, we’ll link to other helpful resources on rankultra.com to guide your blogging journey. Let’s dive in!
📚 For a foundational understanding of SEO, check out our post on Google SEO Basics to complement your GSC knowledge.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Google Search Console?
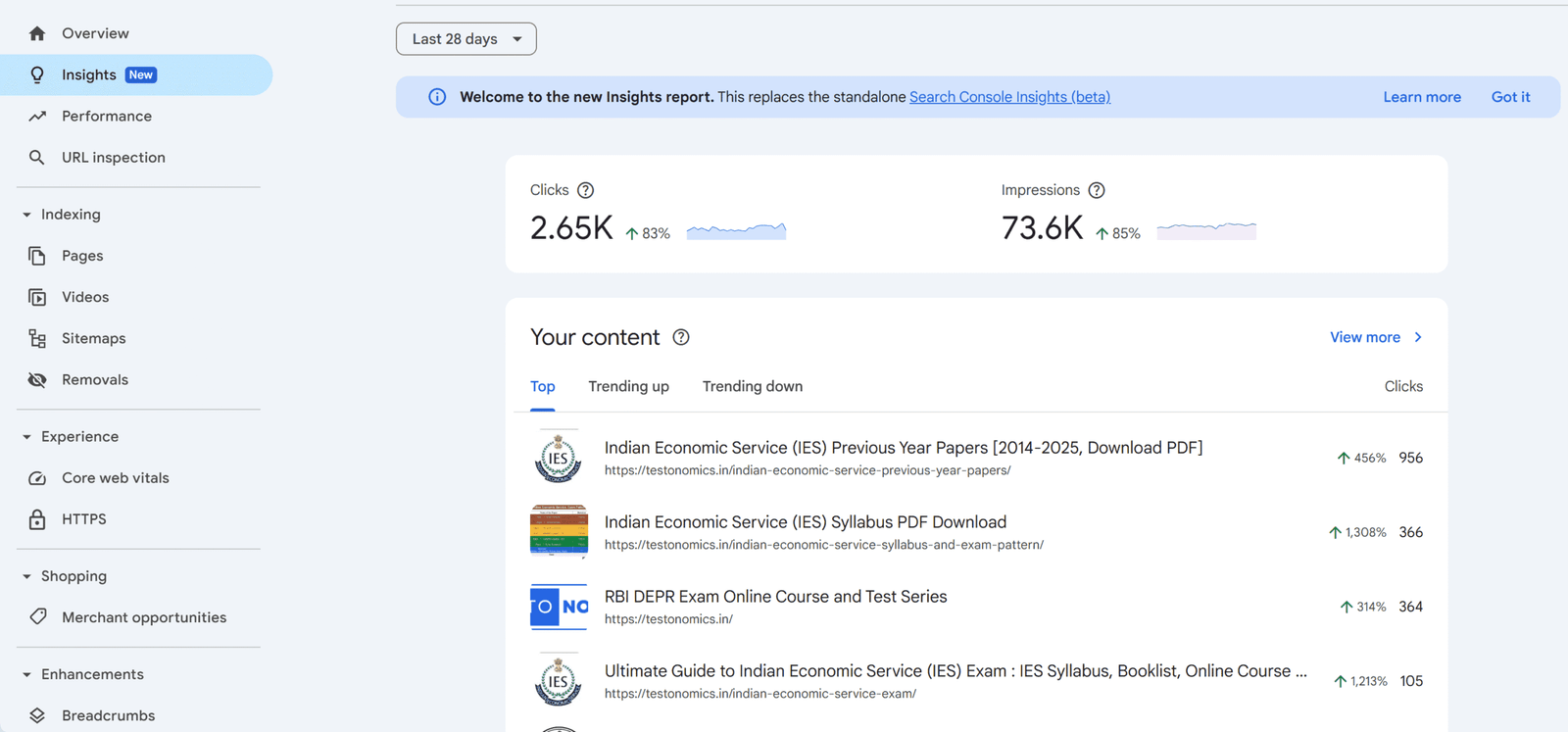
Google Search Console (GSC) is a free tool provided by Google to help website owners, bloggers, and SEO professionals monitor and optimize their site’s presence in Google search results. It offers insights into how Google crawls, indexes, and ranks your pages, making it a cornerstone for website performance tracking. Whether you’re tracking keyword performance, fixing crawl errors, or improving mobile usability, GSC provides the data you need to succeed.
Why Every Website Owner Needs GSC
Track keyword rankings (impressions, clicks, CTR) without third-party tools
Identify indexing issues (e.g., pages blocked by robots.txt, 404 errors)
Submit sitemaps to speed up crawling
Get alerts for security issues or manual penalties
Optimize for Core Web Vitals and mobile usability
GSC helps you understand how users find your blog through search analytics, identify indexing issues, and optimize for better rankings. It’s like a dashboard for your blog’s health, showing you what’s working and what needs improvement. For example, GSC can reveal which keywords drive traffic, helping you refine your content strategy. To learn more about choosing the right keywords, read our guide on How to do Keyword Research.
How Google Search Console Differs from Google Analytics
While both tools provide valuable insights, they serve distinct purposes:
Google Search Console focuses on how your website performs in Google Search. It helps you track keyword rankings, impressions, indexing status, technical SEO errors, and user experience issues that affect your visibility in search.
Google Analytics, on the other hand, focuses on user behavior after people land on your site. It shows you how long users stay, which pages they visit, where they came from (social, direct, email, etc.), and what actions they take.
Unlike tools that estimate rankings or guess at traffic, GSC gives you actual search data: real impressions, real clicks, real positions in Google.
🔍 Google Search Console vs Google Analytics
| Feature | Google Search Console | Google Analytics |
|---|---|---|
| Tracks | Search engine data | On-site user behavior |
| Shows | Clicks, impressions, queries, indexing, errors | Pageviews, bounce rate, session time |
| Audience | Search-focused | Marketing & engagement-focused |
Unlike Google Analytics, which shows what users do after they land on your blog, GSC shows what happens before the click:
How you appeared in search (impressions)
Which queries triggered your pages
Why some pages aren’t indexed or ranking
What technical issues block visibility
Use both Google Search Console and Google Analytics together for a complete SEO picture.
✅ GSC = diagnostic + strategic SEO
✅ GA = user behavior + conversion tracking
🎯 Google’s official documentation on GSC is a great reference to keep open.
Most Important Features of Google Search Console
The most important features of Google Search Console for SEO include Performance Report, URL Inspection Report, Links Report, Sitemaps Report and Core Web Vitals Report.
Performance Report: GSC tracks clicks, impressions, and click-through rates (CTR) for your pages and queries.
URL Inspection Tool: GSC checks if a page is indexed and identifies issues.
Links Report: GSC shows which pages are indexed and highlights crawl errors.
Sitemaps Report: GSC ensures Google can find and crawl your site’s pages.
Mobile Usability Report: GSC identifies issues affecting mobile users.
Core Web Vitals Report: GSC measures user experience metrics like loading speed and visual stability.
If you’re new to SEO terminology, our Google SEO Glossary explains key terms like “indexing” and “crawl errors” in simple language.
Why Google Search Console is Essential for SEO
GSC is a game-changer for search engine optimization because it provides direct insights from Google about your site’s performance. For beginners, it simplifies website health monitoring by highlighting issues like broken links or mobile usability problems. By fixing these, you can improve your rankings and attract more readers. GSC also helps you track keyword performance, optimize content, and ensure your blog is user-friendly.
For a step-by-step guide to starting your blog, visit our post on How to Start a Blog and pair it with GSC for maximum impact.
⚙️ How to Set Up Google Search Console (For WordPress & Non-WordPress Users)
Getting started with GSC is straightforward, even for beginners. Follow these steps to set up GSC for your blog
✅ For WordPress Users: Use the Site Kit Plugin (Easiest Method)
Go to WordPress > Plugins > Add New
Search for Site Kit by Google
Install, activate, and follow the setup wizard
Site Kit will auto-connect Search Console, Google Analytics, and more
🎉 No coding, DNS editing, or HTML uploads needed.
📌 If you’re using RankMath SEO, it also helps you connect to GSC and monitor search performance within WordPress.
🛠️ For Other Platforms: Manual Setup
Create a Google Account: If you don’t have one, sign up at accounts.google.com.
Add Your Property:
Go to search.google.com/search-console.
Choose between Domain (e.g., rankultra.com) or URL prefix (e.g., https://rankultra.com). For beginners, URL prefix is simpler.
Verify Ownership: Prove you own the site using one of these methods:
HTML Tag: Copy a meta tag and add it to your site’s <head> section.
Google Analytics: Link GSC to an existing Analytics account.
DNS Record: Add a TXT record to your domain’s DNS settings (advanced).
Submit and Verify: Follow the prompts to complete verification.
Troubleshooting Setup Issues
Verification Fails: Double-check the HTML tag or DNS record. If using WordPress, plugins like RankMath SEO can simplify this process.
Common Errors: Ensure you’re verifying the correct URL (e.g., include “https://” if applicable).
Beginner Tip: Use the HTML tag method for simplicity, especially if you’re new to blogging.
Then, submit your sitemap:
Go to Indexing > Sitemaps
Enter:
/sitemap.xmlClick Submit
Need help creating a sitemap? If you’re on WordPress, plugins like RankMath or Yoast generate it automatically.
Navigating the Google Search Console Interface
Once set up, GSC’s dashboard provides a wealth of data. Here’s a quick overview of the main sections:
Overview: A snapshot of performance, coverage, and Core Web Vitals.
Performance: Tracks clicks, impressions, and keyword performance.
URL Inspection: Checks individual page status.
Sitemaps: Manages sitemap submissions.
Mobile Usability: Identifies mobile-specific issues.
Core Web Vitals: Monitors user experience metrics.
For a checklist to optimize your blog’s pages, see our On-Page SEO Checklist.
📊 Understanding Key Google Search Console Reports
GSC’s reports are your go-to tools for improving SEO. Let’s break down the most important ones for beginners.
Performance Report
The Performance Report shows how your blog performs in Google search results, including:
Clicks: How many users clicked your links.
Impressions: How often your pages appeared in search results.
CTR: The percentage of impressions that led to clicks.
Average Position: Where your pages rank for specific queries.
How to Use It:
Identify top-performing pages and keywords.
Find low-CTR pages to optimize titles and meta descriptions.
Use filters (e.g., date, country) for targeted insights.
Beginner Tip: Look for high-impression, low-click keywords to improve content relevance. Learn more in our How to do Keyword Research guide.
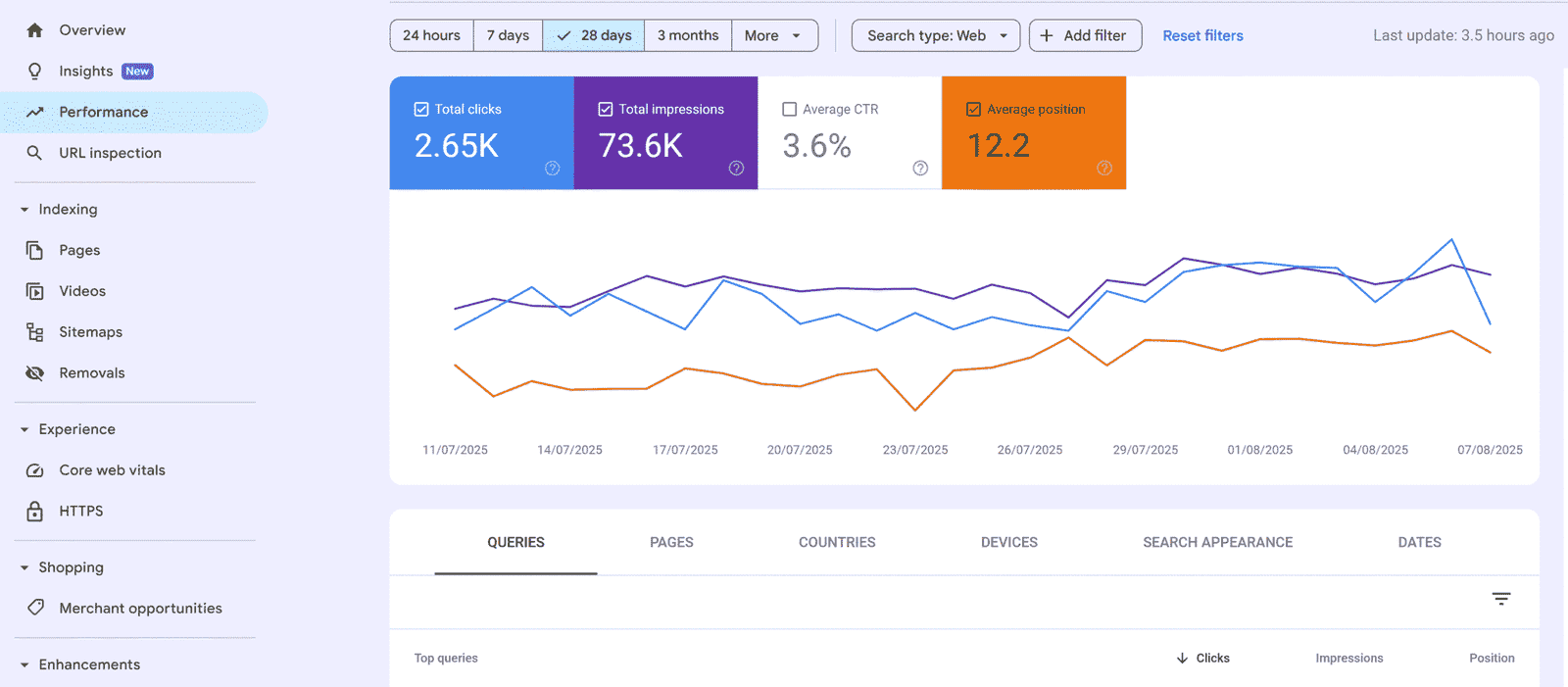
URL Inspection Tool
The URL Inspection Tool lets you check a specific page’s indexing status and request re-crawling.
Use Cases:
Verify if a new post is indexed.
Troubleshoot indexing issues like “URL is not on Google.”
Request Google to re-crawl updated pages.
Actionable Steps:
Enter a URL in the top search bar.
Check for errors (e.g., “Not indexed” or “Blocked by robots.txt”).
Fix issues and click “Request Indexing.”
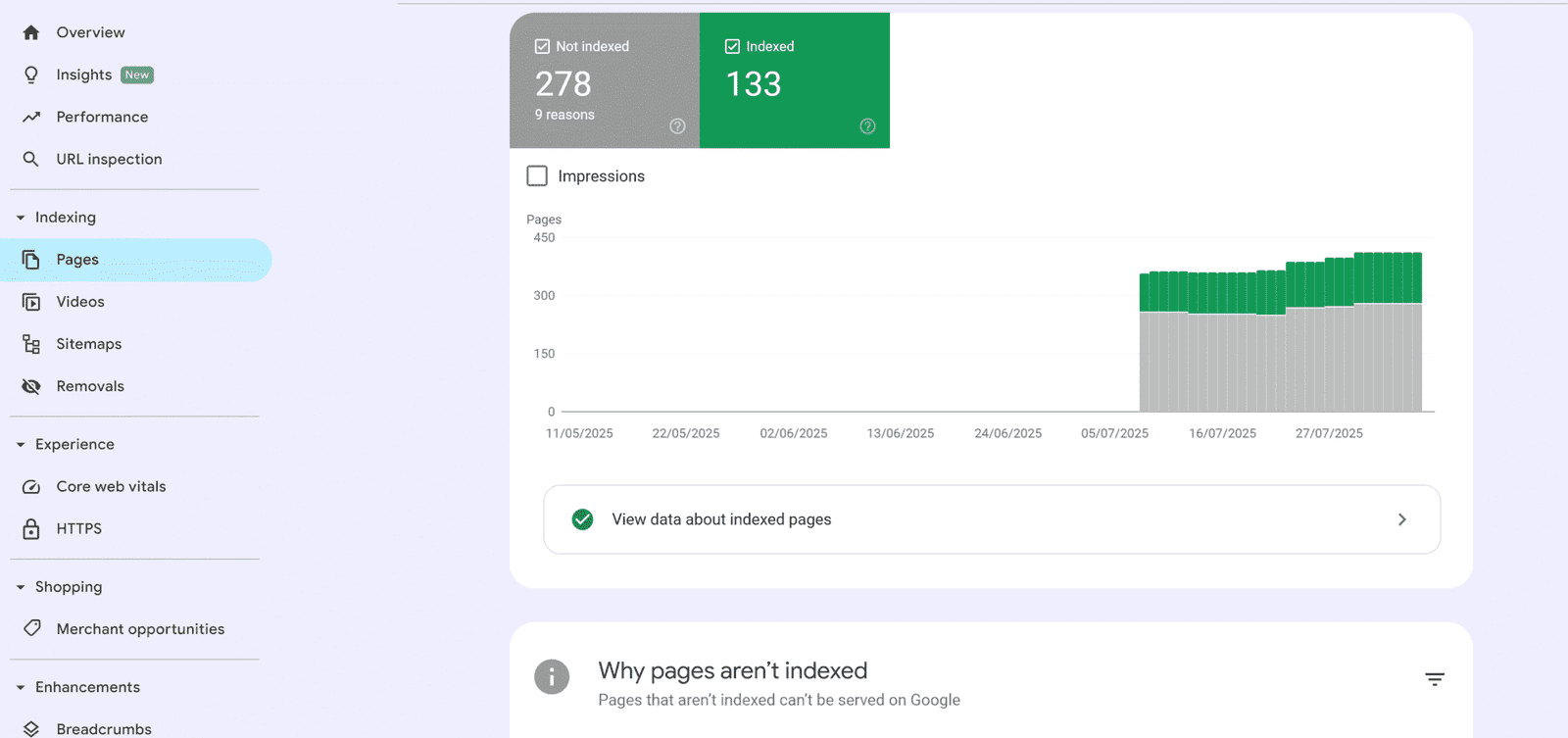
Indexing Report
The Indexing Report lists all pages Google has crawled, categorizing them as:
Valid: Successfully indexed pages.
Error: Pages with 404 error or server errors.
Excluded: Pages intentionally not indexed (e.g., duplicates).
Fixing Common Issues:
404 Errors: Redirect broken links or update URLs.
Duplicate Content: Use canonical tags to specify the preferred page.
Beginner Tip: Regularly check this report to ensure all important pages are indexed.
Sitemaps Report
A sitemap is an XML file that lists your site’s pages, helping Google crawl them efficiently. The Sitemaps Report shows if your sitemap is valid and indexed.
How to Submit a Sitemap:
Create an XML sitemap using tools like Yoast or RankMath SEO.
Upload it to your site’s root directory (e.g., rankultra.com/sitemap.xml).
Submit the URL in GSC under “Sitemaps.”
Troubleshooting: If GSC shows errors, ensure the sitemap is accessible and formatted correctly.
Mobile Usability Report
With Google’s mobile-first indexing, the Mobile Usability Report is critical. It flags issues like small text or unclickable buttons that affect mobile users.
Fixing Issues:
Use responsive design (check your theme settings).
Test your site with Google’s Mobile-Friendly Test.
Improve page speed optimization for mobile users.
To ensure your blog is optimized for all devices, refer to our On-Page SEO Checklist.
Core Web Vitals Report
The Core Web Vitals Report measures user experience metrics:
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP): Loading speed.
Interaction to Next Paint (INP): Interactivity.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS): Visual stability.
Why It Matters: Poor scores can hurt rankings and user retention.
Fixing Issues:
Optimize (Eg: compress to reduce size) images for faster loading.
Minimize JavaScript to improve interactivity.
Use CSS to prevent layout shifts.
🎯 How to Use Google Search Console to Improve Website SEO
GSC isn’t just for monitoring—it’s a powerful tool for search engine optimization. Here’s how beginners can use it to boost their blog’s performance.
You now know what the reports are. Here’s how to use GSC to rank better:
✅ 1. Identify “Almost There” Pages
Filter for keywords ranking in positions 8–20 in SERP. These are Keywords for which your blog is ranking on page 2 of Search Engine Results and reflect low-hanging fruits. With a little improvement in On-Page SEO, Off-Page SEO and technical SEO, you can improve its ranking in SERP and bring it to the first page.
📌 Steps:
Go to Performance > Queries
Filter by average position
Update those pages: better internal linking, new headers, refreshed copy, richer media
Pair with our On-Page SEO Checklist to push them to page-1 of google search results.
✅ 2. Fix Low CTR Titles
Sort by Impressions
Spot pages with high views but low clicks
Rewrite titles/meta to be clearer, more emotional, or question-based
For bloggers, a high CTR means your content is resonating with users at the first impression — your title and meta description are compelling enough to earn the click. Low CTR, even with high impressions, signals that your blog may be visible but not attractive or relevant enough to searchers.
To improve your blog’s CTR, start by writing more attention-grabbing, benefit-driven titles that directly address search intent. Use power words, numbers, questions, or brackets (e.g. [2025 Update]) to stand out. Optimize your meta descriptions to clearly explain what the post offers and why it matters — treat them like mini ads. Including your focus keyword naturally in both the title and meta can also help align with what users are searching for. Testing different title styles (e.g. how-to vs listicle) and monitoring results in Google Search Console can show what works best.
📈 Even a 2% CTR improvement can drive hundreds more visits a month.
✅ 3. Discover New Keyword Angles
Look through unexpected queries. Maybe you rank for “vegan breakfast budget recipes” even though your post was titled “Easy Vegan Meals.”
Now, optimise your blog post for this new keyword by following google basic SEO practices.
🎯 Update content, add an H2, target the secondary query.
✅ 4. Monitor Technical SEO
Make exploring “Pages > Excluded” your weekly habit. Each excluded URL is a lost opportunity. Resolve:
Thin content
Redirect chains
Mobile errors
Crawl budget issues
Use Google SEO Glossary to decode GSC terminology.
🔬 Advanced GSC Use Cases: What Pros Watch Weekly
Advanced Google Search Console users monitor trends weekly to stay ahead of SEO decay, algorithm shifts, and content underperformance. Another high-impact move is identifying keyword cannibalization, where multiple blog posts unintentionally compete for the same search term — this can be resolved by merging, updating, or re-optimizing affected content. These advanced use cases turn GSC from a basic tracking tool into a powerful SEO control center.
1. Content Decay Detection
Compare last 3 months vs previous. Posts losing impressions or clicks = content decay.
🛠 Refresh them:
Add newer examples
Embed video
Update stats
Improve page load speed
2. Detect Keyword Cannibalization
Two posts ranking for the same keyword?
That splits traffic.
Use the “Compare URLs” feature in Performance. Decide:
Merge them
Canonicalize one
Shift keyword targeting
3. Segment by Country or Device
If your traffic is mostly mobile, optimize for smaller screens.
If your audience is global, check ranking differences per region.
🌍 Local bloggers: focus on country-specific insights.
4. Diagnose Google’s Behavior
Is Google crawling but not indexing? That often signals:
Thin content
Lack of internal links
Duplicate structure
Fix → Inspect → Resubmit → Track.
🧪 Real Example: From “Discovered – Not Indexed” to 5,000 Views
I worked with a food blogger who had 40+ posts in “Discovered – not indexed” for over a month.
Here’s what we did:
Added each post to the sitemap
Linked from existing indexed posts
Updated intro paragraphs with stronger keyword usage
Reduced CLS issues via theme optimization
Requested indexing manually
📈 Within 7 days, 38 out of 40 were indexed
📈 6 weeks later, 4 of them broke into the top 10 for high-volume keywords
🧱 Common Google Search Console Issues & What To Do
| Issue | Why It Happens | Fix |
|---|---|---|
| Discovered – not indexed | Google found it but didn’t crawl | Add internal links, submit sitemap |
| Crawled – not indexed | Crawled but low quality or duplication | Improve content, make unique |
| Soft 404 | Thin or broken content | Expand value, fix layout |
| Mobile usability | Fonts too small, buttons too close | Use responsive theme |
| Core Web Vitals | LCP, CLS, FID too slow | Optimize images, remove layout shift |
🧠 GSC Isn’t Enough (But It’s Where You Start)
Google Search Console doesn’t:
Show competitor data
Offer keyword research tools
Track traffic from Bing, Pinterest, or email
But it does give you first-party, real-time SEO data from Google. No guesswork. No estimations.
Integrating Google Search Console with Other Tools
GSC works best when paired with other tools:
Ahrefs or Ubersuggest for keyword discovery
Google Analytics for user engagement
RankMath SEO to optimize your posts right inside WordPress
📚 Further Learning & Resources
If you want to level up:
And from our site:
✅ Final Thoughts: Build the Habit, Not Just the Setup
Setting up Google Search Console is easy. Using it regularly — that’s the difference between flatline traffic and steady growth.
Add a weekly GSC review to your blog workflow
Check for indexing issues, keyword trends, and UX flags
Let GSC guide your next blog update, not random guesswork
GSC won’t grow your blog alone — but it will tell you exactly what’s standing in the way.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
❓1. What is the difference between Google Search Console and Google Analytics?
Answer: Google Search Console (GSC) shows you how your site performs in Google Search — it tracks keyword rankings, impressions, clicks, and indexing issues. Google Analytics (GA) shows what users do after they land on your site — like how long they stay, which pages they visit, and what actions they take. Use GSC to improve visibility in search and GA to analyze user behavior and conversions.
❓2. Why is my blog post not indexed in Google Search Console?
Answer: If a blog post is listed as “Discovered – not indexed” or “Crawled – not indexed,” it usually means the content is thin, lacks internal links, or wasn’t deemed valuable enough by Google. To fix it: add helpful content, link to it from existing posts, ensure it’s included in your sitemap, and request indexing using the URL Inspection Tool in GSC.
❓3. How can I use Google Search Console to increase blog traffic?
Answer: Use the Performance report to find keywords your blog ranks for and improve your content around them. Identify posts with high impressions but low CTR — then update titles and meta descriptions to boost clicks. Also, use the Pages report to find and fix indexing issues, and the Links report to improve internal linking, both of which help boost visibility and rankings.
❓4. Do I need to check Google Search Console every day?
Answer: No, a weekly check-in is ideal for most bloggers. Look for trends in clicks/impressions, monitor indexing issues, and track new posts’ performance. Set email alerts for major issues like coverage errors or manual actions. Making GSC part of your weekly content optimization routine is enough to catch problems early and guide your SEO strategy.
❓5. Is Google Search Console enough for SEO? Do I need other tools too?
Answer:
Google Search Console is a powerful free SEO tool, but it has limitations. It doesn’t provide keyword research, competitor analysis, or backlink quality metrics. For a more complete SEO strategy, pair GSC with tools like RankMath SEO (for on-page optimization), Google Analytics (for user behavior), and paid tools like Ahrefs or Ubersuggest if budget allows. For most beginners, though, GSC covers the core essentials.
